
Laplace
French mathematician, astronomer, geometer, and physicist of the Enlightenment, Pierre-Simon Laplace was born on the 23rd of March year 1749 in Beaumont-en-Auge, Normandy. He contributed a lot to the knowledge of Celestial mechanics and Statistical theory, making tremendous progress in unveiling the cosmos and the math structure of the universe.
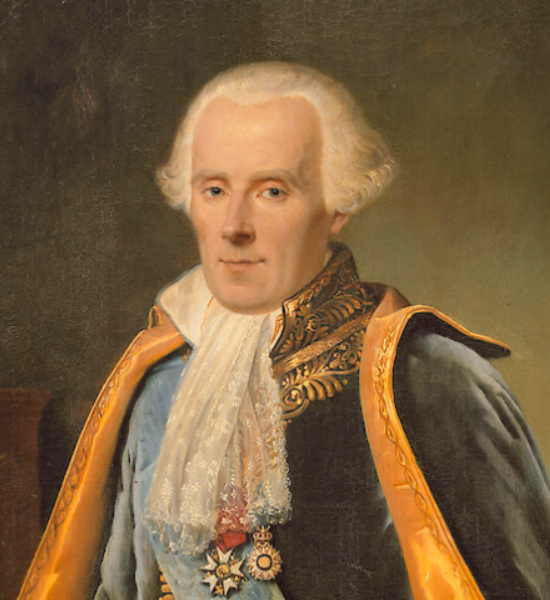

Laplace’s contributions placed him as one of the most important iconic intellectuals of the eighteenth century. He contributed these views where he wrote about the mechanics regarding celestial bodies to offer a mathematical rigour towards the theme of the well-ordering of the universe.
Laplace received his early education at the Collège de Beaumont and then at the Collège Mazarin, Paris, where he developed his mathematical education. They anticipating molded him for a great science career.

His major focus in his later part of his career was celestial mechanics and this was the climax of his carrier. His work “Celestial Mechanics” (1799–1825) dealt with the stability of solar system mathematically. He also established forward leaps in probability theory, fluid mechanics as well as in the study of gravitation.


Despite the fact that Laplace predating space exploration, his theoretical context provided a backbone in the study of the celestial objects’ motion. His inspiration still affects astronomers and space science professionals.
Laplace received many honors and also had position in the government, for instance became a Minister of the Interior for Napoleon Bonaparte. His name is perpetuated in the Laplace function and the Laplace transform; thus, it is evident how much he influenced mathematics.
Laplace was a man of details and few emotions; thus, he survived the French Revolution. He kept focusing on science and its procedures regardless of the political changes.
Pierre-Simon Laplace was a French mathematician whose main contributions are present in the mathematical sciences in general, as well as celestial mechanics, in particular. Today and in the future, his visionary work remains relevant to instill knowledge about the universe to the scholars. The techniques that he came up with are still used to this very day in efforts to solve outer space mystery and understand the universe.